—–作業四—–
1. Selling Currency Call Options. Mike Suerth sold a call option on Canadian dollars for $0.01 per unit. The strike price was $.76, and the spot rate at the time the option was exercised was $.82. Assume Mike did not obtain Canadian dollars until the option was exercised. Also assume that there are 50,000 units in a Canadian dollar option. What was Mike’s net profit on the call option?
Mike is call options seller.
ST=0.82, X=0.76
Use 0.01*50,000=500 to sell the right.
| ST | X | Min | inflows | Premium | Total | Buy Canadian dollars at market price | net profit (or loss) |
| 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.76 | +38,000 | +500 | +38,500 | -41,000 | -2,500 |
3. Speculating with Currency Put Options. Alice Duever purchased a put option on British pounds for $.04 per unit. The strike price was $1.80 and the spot rate at the time the pound option was exercised was $1.59. Assume there are 31,250 units in a British pound option. What was Alice’s net profit on the option?
Alice is put options buyer.
ST=1.59, X=1.80
Pay 0.04*31,250=1,250 to buy the right.
Max(ST, X) to sell FC.
| ST | X | Max | Inflow | Premium | net inflow | Buy British pounds at market price | net profit |
| 1.59 | 1.80 | 1.80 | +56,250 | -1,250 | +55,000 | -49,687.5 | +5,312.5 |
4. Speculating with Currency Put Options. Bulldog, Inc., has sold Australian dollar put options at a premium of $.01 per unit, and an exercise price of $.76 per unit. It has forecasted the Australian dollar’s lowest level over the period of concern as shown in the following table. Determine the net profit (or lose) per unit to Bulldog, Inc., if each level occurs and the put options are exercised at that time.
Bulldog, Inc. is put options seller.
X=0.76
Use 0.01 to sell the right.
| ST | X | Max | outflow | Premium | net outflow | Sell Australian dollar at market price | net profit (or loss) |
| 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.76 | -0.76 | +0.01 | -0.75 | +0.72 | -0.03 |
| 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.76 | -0.76 | +0.01 | -0.75 | +0.73 | -0.02 |
| 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.76 | -0.76 | +0.01 | -0.75 | +0.74 | -0.01 |
| 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.76 | -0.76 | +0.01 | -0.75 | +0.75 | 0 |
| 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | -0.76 | +0.01 | -0.75 | +0.76 | 0.01 |
5. Speculating with Currency Call Options. Randy Rudecki purchased a call option on British pounds for $.02 per unit. The strike price was $1.45 and the spot rate at the time the option was exercised was $1.46. Assume there are 31,250 units in a British pound option. What was Randy’s net profit on this option?
Randy is call options buyer.
ST=1.46, X=1.45
Pay 0.02*31,250=625 to buy the right.
Min(ST, X) to buy FC.
| ST | X | Min | Cost | Premium | net inflow | Sell British pounds at market price | net profit (or loss) |
| 1.46 | 1.45 | 1.45 | -45,312.5 | -625 | -45,937.5 | +45,625 | -312.5 |
8. Speculating with Currency Put Options. Auburn Co. has purchased Canadian dollar put options for speculative purposes. Each option was purchased for a premium of $.02 per unit, with an exercise price of $.86 per unit. Auburn Co. will purchase the Canadian dollars just before it exercises the options (if it is feasible to exercise the options). It plans to wait until the expiration date before deciding whether to exercise the options. In the following table, fill in the net profit (or loss) per unit to Auburn Co. based on the listed possible spot rates of the Canadian dollar on the expiration date.
Auburn Co. is put options buyer.
X=0.86
Pay 0.02 to buy the right.
Max(ST, X) to sell FC.
| ST | X | Min | Inflow | Premium | net inflow | Buy Canadian dollar at market price | net profit (or loss) |
| 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.86 | +0.86 | -0.02 | +0.84 | -0.76 | 0.08 |
| 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.86 | +0.86 | -0.02 | +0.84 | -0.79 | 0.05 |
| 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.86 | +0.86 | -0.02 | +0.84 | -0.84 | 0 |
| 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.87 | +0.87 | -0.02 | +0.85 | -0.87 | -0.02 |
| 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.89 | +0.89 | -0.02 | +0.87 | -0.89 | -0.02 |
| 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.91 | +0.91 | -0.02 | +0.89 | -0.91 | -0.02 |
—–作業五—–
皆不考慮交易成本
1. Central Bank quotes the following for the British pound and the China CNY:
| Quoted Bid Price | Quoted Ask Price | |
| Value of a British Pound in NTD | 50.33 NTD | 50.66 NTD |
| Value of a China CNY in NTD | 4.963 NTD | 5.125 NTD |
| Value of a British Pound in China CNY | 9.7195 CNY | 9.75 CNY |
Assume you have NTD 10,000 to conduct triangular arbitrage. What is your profit from implementing this strategy?
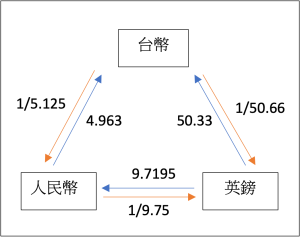
順時針:
NTD 10,000換成10,000*1/50.66=197.394英鎊
197.394英鎊換成197.394*9.7195=1,918.571人民幣
1,918.571人民幣再換回1,918.571*4.963=9,521.868新台幣
此操作會損失新台幣478.132元,沒有套利。
逆時針:
NTD 10,000換成10,000*1/5.125=1,951.220人民幣
1,951.220人民幣換成1,951.220*1/9.75=200.125英鎊
200.125英鎊再換回200.125*50.33=10,072.291新台幣
此操作會增加新台幣72.291元,有套利。
2. 請問以下的報價是否有套利空間? 如果有,如何操作?
Euro/USD=1.2
Euro/Pound=0.8
Pound/USD=1.4

假設有100歐元
如果先換成100*0.8=80英鎊,再換成80*1.4=112美元
上圖中的ask=112/100=1.12
∵bid > ask
∴有套利空間
3. 試根據下列數據回答以下問題:
即期匯率 30.0 NT/US
遠期匯率 30.5 NT/US(90 天期遠期外匯)
預期匯率 30.3 NT/US(90 天期)
台灣利率 5%
美國利率 3%
(1) 此例中有拋補的利率平價說是否成立?
id = if +(F-E)/E * 12/D
5% ≠ 3%+(30.5-30)/30*12/3
∴有拋補的利率平價說不成立
(2) 依據未拋補的利率平價理論,你應該選擇新台幣存款或美元存款?
id = if +(Eet+1-Et)/Et
5% > 3%+(30.3-30)/30=4%
∵台灣利率大於美國利率
∴選新台幣存款
—–作業六—–
1. 摘錄第 11、12 週課程影片重點筆記,請每人每週各出 10 題選擇題共 20 題(超過者扣分),並附上正確答案,做為期末考題庫。
2. 範圍涵蓋整個課程、答案正確者分數為滿分。
3. 不出計算題,但可以有數學概念。
<筆記>




<期末考題庫>
D 1. 下列何者非因匯率變動而產生之風險?
A. 交易風險
B. 經濟風險
C. 換算風險
D. 信用風險
D 2. 下列何者為契約避險可以使用的金融工具?
A. 遠期外匯
B. 外匯期貨
C. 外匯選擇權
D. 以上皆是
A 3. A公司出口商品到美國,依契約內容,買方將於90天後支付100萬元,請問A公司可能因匯率變動而面臨什麼風險?
A. 交易風險
B. 經濟風險
C. 換算風險
D. 無風險
D 4. 下列哪種操作可以規避匯率變動的風險?
A. 提前或延後
B. 風險移轉
C. 風險分攤
D. 以上皆是
A 5. 換算風險又稱為?
A. 會計風險
B. 營運風險
C. 管理風險
D. 匯率風險
B 6. 子公司用來營運和收支的貨幣為?
A. 虛擬貨幣
B. 功能性貨幣
C. 報表貨幣
D. 法定貨幣
C 7. 母公司編製財務報表所使用的貨幣為?
A. 虛擬貨幣
B. 功能性貨幣
C. 報表貨幣
D. 法定貨幣
D 8. 匯率變動較不會影響下列何者?
A. 兩國商品的相對價格
B. 兩國生產要素的相對價格
C. 金融市場的融資利率
D. 企業員工的薪水
D 9. 下列何者非換算風險管理的換算方法?
A. 時序法
B. 現行匯率法
C. 流動及非流動法
D. 直接換算法
B 10. 因不可預期的匯率變動對企業市場價值所造成的影響為下列哪一種風險?
A. 交易風險
B. 經濟風險
C. 換算風險
D. 管理風險
A 11. 根據效率市場假說,過去及目前所有大眾和私有的資訊已充分反映於價格上稱之為何?
A. 強式效率市場
B. 半強式效率市場
C. 弱式效率市場
D. 以上皆非
A 12. 下列對於弱式效率市場的敘述何者錯誤?
A. 內線消息無效
B. 技術分析無效
C. 基本面分析有效
D. 反應所有歷史資訊
A 13. 根據效率市場假說,在何種效率市場下,內線無效?
A. 強式效率市場
B. 半強式效率市場
C. 弱式效率市場
D. 以上皆非
D 14. 下列何者不是匯率預測的方法?
A. 計量經濟預測法
B. 技術分析
C. 基本分析
D. 統計分析
B 15. 根據過去的匯率與外匯成交量資料,找出匯率變化的特定型態來預測匯率的未來變動,為下列哪一種預測方法?
A. 計量經濟預測法
B. 技術分析
C. 基本分析
D. 統計分析
A 16. 利用經濟理論界定匯率及其解釋變數之間的迴歸式,並以統計方法與歷史資料求出匯率及其解釋變數之間的關係,再根據此一關係進行匯率預測,為下列哪一種預測方法?
A. 計量經濟預測法
B. 技術分析
C. 基本分析
D. 統計分析
C 17. 下列何者非技術分析的指標?
A. 相對強弱指標
B. 隨機指標
C. 經濟成長指標
D. 趨向指標
D 18. 計量經濟預測法的步驟包含以下哪些?
A. 利用經濟理論確立匯率的迴歸模型
B. 以統計方法及歷史資料求出迴歸模型的相關係數
C. 以求出的迴歸模型預測匯率
D. 以上皆是
A 19. 以統計模型來說,在橫斷面的迴歸模式習慣用哪一種「預測」?
A. predict
B. forecast
C. guess
D. expect
B 20. 以統計模型來說,在縱貫面的迴歸模式習慣用哪一種「預測」?
A. predict
B. forecast
C. guess
D. expect
