連結題目
20.Deriving Forecasts of the Future Spot Rate
As of today, assume the following information is available:

a. Use the forward rate to forecast the percentage change in the Mexican peso over the next year.
b. Use the differential in expected inflation to forecast the percentage change in the Mexican peso over the next year.
c. Use the spot rate to forecast the percentage change in the Mexican peso over the next year.
a. (0.19-0.20)/0.20=-0.05 MXN會貶值5%
b. 11%-15%=-4% MXN會貶值4%
c. 2%-2%=0
24.IFE
Beth Miller does not believe that the international Fisher effect (IFE) holds. Current one-year interest rates in Europe are 5 percent, while one-year interest rates in the U.S. are 3 percent. Beth converts $100,000 to euros and invests them in Germany. One year later, she converts the euros back to dollars. The current spot rate of the euro is $1.10.
a. According to the IFE, what should the spot rate of the euro in one year be?
b. If the spot rate of the euro in one year is $1.00, what is Beth’s percentage return from her strategy?
c. If the spot rate of the euro in one year is $1.08, what is Beth’s percentage return from her strategy?
d. What must the spot rate of the euro be in one year for Beth’s strategy to be successful?
a.1.10*{(1+0.03)/(1+0.05)}= $1.079
b. USD 換 EUR: $100,000/1.10 = EUR 90,909.091 存入歐洲銀行
可收回:EUR90,909.091*1.05=EUR95,454.546
換回美元 :$95,454-546
收益為($95,454.546 -$100,000)/$100,000=-4.545%
c. 前面跟b一樣
EUR95,454.546*1.08=$103,090.91
收益為($103,090.91/100,100)-1=3.09%
d. 一年後即期匯率大於1.079
25.Integrating IRP and IFE
Assume the following information is available for the U.S. and Europe:
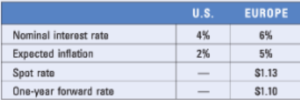
a. Does IRP hold?
b. According to PPP, what is the expected spot rate of the euro in 1 year?
a.(1.1 – 1.13)/1.13 不等於6% – 4%/1+4%→ IRP 不成立
b.5% – 2%/1+2% =0.029=2.9%
預期即期匯率=1.13*(1-2.9%)=1.097
26.IRP
The one-year risk-free interest rate in Mexico is 10%. The one-year risk-free rate in the U.S. is 2%. Assume that interest rate parity exists. The spot rate of the Mexican peso is $.14.
a. What is the forward rate premium?
b. What is the one-year forward rate of the peso?
c. Based on the international Fisher effect, what is the expected change in the spot rate over the next year?
d. If the spot rate changes as expected according to the IFE, what will be the spot rate in one year?
e. Compare your answers to (b) and (d) and explain the relationship.
墨西哥的無風險利率為10%,美國的無風險利率為2%,IRP 成立的話,墨西哥peso的即期匯率為 0.14
a. (1+0.02)/(1+0.1) -1 = -0.07273
b. 0.14*(1-0.07273)=0.1298
c. 同a
d. 同b
f.一年後遠期=即期,兩者平價
39.PPP and Real Interest Rates
The nominal (quoted) U.S. one-year interest rate is 6 percent, while the nominal one-year interest rate in Canada is 5 percent. Assume you believe in purchasing power parity. You believe the real one-year interest rate is 2 percent in the United States, and that the real one-year interest rate is 3 percent in Canada. Today the Canadian dollar spot rate is$.90.What do you think the spot rate of the Canadian dollar will be in one year?
(2%-5%)/(1+5%)=-2.85%
一年後即期匯率=0.9*(1-2.85%)=0.874
44.IFE and Forward Rate.
The one-year Treasury (risk-free) interest rate in the U.S. is presently 6%, while the one-year Treasury interest rate in Switzerland is 13%. The spot rate of the Swiss franc is $.80. Assume that you believe in the international Fisher effect. You will receive 1 million Swiss francs in one year.
a. What is the estimated amount of dollars you will receive when converting the francs to U.S. dollars in one year at the spot rate at that time?
b. Assume that interest rate parity exists. If you hedged your future receivables with a one-year forward contract, how many dollars will you receive when converting the francs to U.S. dollars in one year?
a.遠期=[(1+6%)/(1+13%)]-1 =-0.062
1,000,000法郎*0.8*(1-0.062)=$774,400
1,000,000*0.8=$800,000
$774,400-$800,000=$-25,600
b. 1,000,000*0.8=$800,000
皆不考慮交易成本
5.Central Bank quotes the following for the British pound and the China CNY:
Quoted Bid Price Quoted Ask price
Value of a British Pound in NTD 50.33 NTD 50.66 NTD
Value of a China CNY in NTD 4.963 NTD 5.125 NTD
Value of a British Pound in China CNY 9.7195 CNY 9.75 CNY
Assume you have NTD 10,000 to conduct triangular arbitrage. What is your profit from implementing this strategy?
NTD-CNY 1/5.125 ,CNY-GBP 1/9.75 ,GBP-NTD 50.33
10,000/5.125/9.75*50.33=10,072.3 大概賺72塊錢左右
1.Covered Interest Arbitrage in Both Directions. The following information is available:
• You have $500,000 to invest
• The current spot rate of the Moroccan dirham is $.110.
• The 60-day forward rate of the Moroccan dirham is $.108.
• The 60-day interest rate in the U.S. is 1 percent.
• The 60-day interest rate in Morocco is 2 percent.
a. What is the yield to a U.S. investor who conducts covered interest arbitrage? Did covered interest arbitrage work for the investor in this case?
b. Would covered interest arbitrage be possible for a Moroccan investor in this case?
a. $500,000*1.01=$505,000
$(500,000/0.11)*1.02*0.108 =$500,727.27
在美國定存獲利高於在摩洛哥定存,故不適用
b. 對摩洛哥的投資者來說適用。
10.Covered Interest Arbitrage. Assume the following information:
Spot rate of Mexican peso = $.100
180 day forward rate of Mexican peso= $.098
180 day Mexican interest rate= 6%
180 day U.S. interest rate= 5%
Given this information, is covered interest arbitrage worthwhile for Mexican investors who have pesos to invest? Explain your answer.
設墨西哥投資者有100,000披索(=$10,000)
墨西哥定存 100,000披索*1.06=106,000披索*0.98*0.1=$10,388
美國定存 $10,000*1.05=$10,500
墨西哥投資者在美國投資獲利較高,值得投資。
16.Triangular Arbitrage. Assume the following information:
Quoted Price
Value of Canadian dollar in U.S. dollars $.90
Value of New Zealand dollar in U.S. dollars $.30
Value of Canadian dollar in New Zealand dollars NZ$3.02
Given this information, is triangular arbitrage possible? If so, explain the steps that would reflect triangular arbitrage, and compute the profit from this strategy if you had $1,000,000 to use. What market forces would occur to eliminate any further possibilities of triangular arbitrage?
將USD換成CAD,CAD換成NZD,NZD再換回USD
$(1,000,000/0.9)*3.02*0.3=$1,006,666.67
三角套利存在
加拿大幣對美元的匯率上升、加拿大幣對於紐西蘭幣的匯率下跌、紐西蘭幣對美元的匯率等下跌會使套利機會減少
國際金融市場
財務管理»資金的轉移
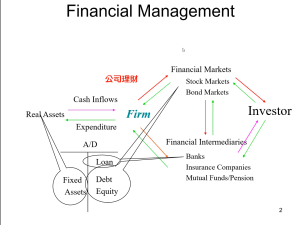
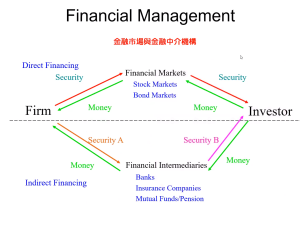
臺灣存託憑證(Taiwan Depositary Receipt,TDR),又稱「第二上市」,指該企業已經在國外上市,另外在臺灣證券交易所申請上市,以存託憑證掛牌,進行募資。此存託憑證持有者和該公司普通股的投資者享有相同的權利和義務。
外匯市場
1.歷史
- 金本位制(1876-1913)
- 布列敦森林協議(1944) 固定匯率
- 浮動匯率(1973)
2.外匯交易
- 現貨(即期)市場:三大交易市場東京、紐約、倫敦,主要是銀行間報價。
- 交叉匯率是兩個非美元間的匯率
- 往來銀行
- 報價上有競爭力
- 與其他銀行的關係
- 未來預測
3.外匯報價
- 各銀行在現貨市場的互動、消除差異
- 買賣價差=(賣出價-買進價)/賣出價
4.匯率的報價影響價差
- 銀行訂單
- 庫存成本
- 銀行競爭成本
- 持有量
- 貨幣風險
5.報價種類
- 直接報價:一塊美元值31塊台幣
- 間接報價:一塊台幣可換1/32塊的美元銀行用31塊台幣跟你買一塊美金
銀行用32塊台幣賣你一塊美金(就是你要用32塊買一塊美金)
6.遠期契約、期貨、選擇權市場
- 避險
- 特徵
- 指定貨幣
- 買或賣 數量/價格/時間
7.影響匯率因素
- 相對通膨率
- 相對利率(費雪)
- 相對所得水平
- 政府管制:對匯率或貿易設立障礙
- 未來預期:外匯市場對任何新聞的反應都可能產生影響
- 交互影響
國際貨幣市場
1.起源與發展
- 境外貨幣(Eurocurrency):在發行該貨幣的國家,不同國家/地區國際銀行的貨幣定期存款,例如境外美元是美元在美國以外的銀行的存款(Euro為境外之意,存款銀行不一定要在歐洲)
- 亞元市場
- 市場利率比較圖
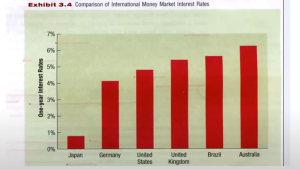
2.全球銀行規範
- Single European Act (1992)
- Basel Ⅰ (1987)
- Basel Ⅱ (2004)
- Basel Ⅲ (2023)
境外貨幣市場
國際貨幣市場的核心是境外貨幣市場(Eurocurrency market) ,境外貨幣是指在發行該貨幣的國家,不同國家/地區國際銀行的貨幣定期存款。
例如,境外美元是美元在美國以外的銀行的存款,境外英鎊是英鎊在英國以外的銀行的存款,而境外日元是日元在日本以外的銀行的存款。前面Euro有點用詞不當,因為存款所在的銀行不必位於歐洲存款銀行可能位於歐洲、加勒比地區或亞洲這個詞是境外。
境外貨幣市場是一個外部銀行系統,與發行該貨幣的國家的國內銀行系統平行運行。
兩個銀行系統都從存入的資金中尋找存款並向客戶提供貸款。
在美國,銀行受聯邦儲備條例的約束,規定了銀行定期存款的準備金要求。此外,美國銀行必須為存入資金支付 FDIC 保險費。另一方面,境外美元存款不受這些準備金要求或存款保險的約束,因此營運成本更低。由於成本結構的降低,境外貨幣市場光其是境外美元市場自成立以來發展迅猛。
報價期限從一天到一年不等,但標準到期日通常是1、2、3、6、9、12個月
境外信貸
Eurocredits 是境外銀行向企業、主權政府、非主要銀行或國際組織提供的短期至中期境外貨幣貸款,貸款以境外銀行本國貨幣以外的貨幣計價。
由於這些貸款通常太大而單個銀行無法處理,境外銀行將聯合起來組成一個聯貸(syndicate)來分擔風險。
遠期利率協定
境外銀行在接受境外存款和延長歐洲信貸方面,面臨的主要風險是存款和信貸期限不匹配導致的利率風險。
例如,如果存款期限長於信用期限,並且利率下降,則在銀行仍支付較高存款利率的同時,信用利率將下調。
相反,如果存款期限短於信貸期限,並且利率上升,則存款利率將向上調整:而銀行仍獲得較低的信貸利率。只有當存款和信貸期限完美匹配時 Eurocredits的展期功能才能讓銀行獲得所需的存貸利差。
遠期利率協議(RFA)是一種銀行間合同,允許境外銀行避險不匹配存款和信貸的利率風險。
境外票據
Euronotcs是由一組國際投資或商業銀行承銷的短期票據,稱為“facility”。客戶借款人與一家機構達成協議,以自己的名義發行境外票據,期限一般為3至10年。
Euronotes 以低於面值的價格出售,並在到期時償還全部面值 •
Euronotes:的期限通常為3至6個月。借款人發現境外票據具有吸引力 因為與歐洲銀行銀團貸款相比,利息費用通常略低 (通常是 LIBOR 加1/8%:)
國際債券市場
債券類型
- 直接固定利率債券
-
- 境外中期票據
- 發行主體: Euro-MTN通常由公司發行。
- 固定利率票券: Euro-MTN是固定利率票券,其期限範圍從不到一年到大約10年不等。
- 定期支付票面利息: 與固定利率債券一樣,Euro-MTN在定期日期支付票面利息。
- 連續發行: 與一次性投放市場的債券發行方式不同,Euro-MTN通常以連續發行方式進行。每次發行部分債券,這種方式使得借款人能夠在需要時靈活地獲得資金。
- 流行的籌資方式: 自1986年首次推出以來,Euro-MTN已經成為一種非常流行的中期資金籌集方式。
- Euro-MTN的彈性發行結構和固定利率使其成為企業籌措中期資金的一種選擇。
- 浮動利率票券 : 第一個浮動利率票券(Floating-rate notes, FRNs)於 1970年推出,浮動利率票券通常是中期債券,其票面支付與某個參考利率掛鉤,常見的參考利率是三個月或六個月的美元
- 股票相關債券
- 可轉換債券(Convertible Bonds):
- 允許投資者將債券轉換成發行人預定數量的股權。
- 可轉換債券的底值是其固定利率債券價值。
- 投資者通常願意接受較低的票面利率,因為他們看中轉換成股票的吸引力。
- 附認股權證債券(Bonds with Equity Warrants):
- 可視為帶有買權功能的固定利率債券。
- 認股權證使債券持有人有權在預定時間段內以預定價格購賞發行人的一定數量的股權。
- 雙元貨幣債券(1980年代流行): 以一種貨幣發行的直接固定利率債券,以該貨幣支付票面利率,到期時的本金則由另一種貨幣償還。
國際債券市場評級
- 惠御評級、穆迪投資者服務公司、標準普爾全球評級
國際債券市場指數
國際股票交易
- 境外發行股票
- 非美國公司發行境外股票:American Depository Receips(ADR)
- 國外股票市場投資: 當地經濟狀況、貨幣走勢、資產投資組合多元化
- 股票市場的特徵
- 國家的法律
- 股東的法律
- 政府政策
- 國家企業是否腐敗
- 財務資訊接露程度
- 股份交叉上市 Cross-Listing of Shares:指公司的股票除了在本國的證交所上市,也在一個或多個外國證交所上市(跨國公司經常交叉上市,但非跨國公司也會交叉上市)
- 洋基股票發行 Yankee Stock Offering:是在美國債券市場上發行的外國債券,即美國以外的政府、金融機構、工商企業和國際組織在美國國內市場發行的、以美元為計值貨幣的債券。
- 美國存託憑證(American Depositary Receipt,ADR)是一種代表在美國以外地區發行的股票的金融工具。
- 定義: ADR是由美國銀行或其他金融機構發行的憑證,代表著在外國上市的股票。
- 用途: ADR的主要目的是讓美國投資者能夠方便地投資和交易在其他國家上市的股票,而無需直接購買外國股票。
- 分級:
- 第一級:最基本的類型,發行人不是為了尋求在美國籌集新股本,不可在納斯達克上市
第二級:發行人不是為了尋求在美國籌集新股本,此類美國存託憑證可以在納斯達克、紐約證交所、美國證券交易所上市
第三級:發行人在美國公開發行新股並在納斯達克、紐約證交所、美國證券交易所上市
- 第一級:最基本的類型,發行人不是為了尋求在美國籌集新股本,不可在納斯達克上市
- 全球註冊股份
- 國際股票市場基準
